Sorting Algorithms
Sorting algorithms are a fundamental part of computer science. They are used to sort data in a particular order, whether it be in increasing order, or decreasing order.
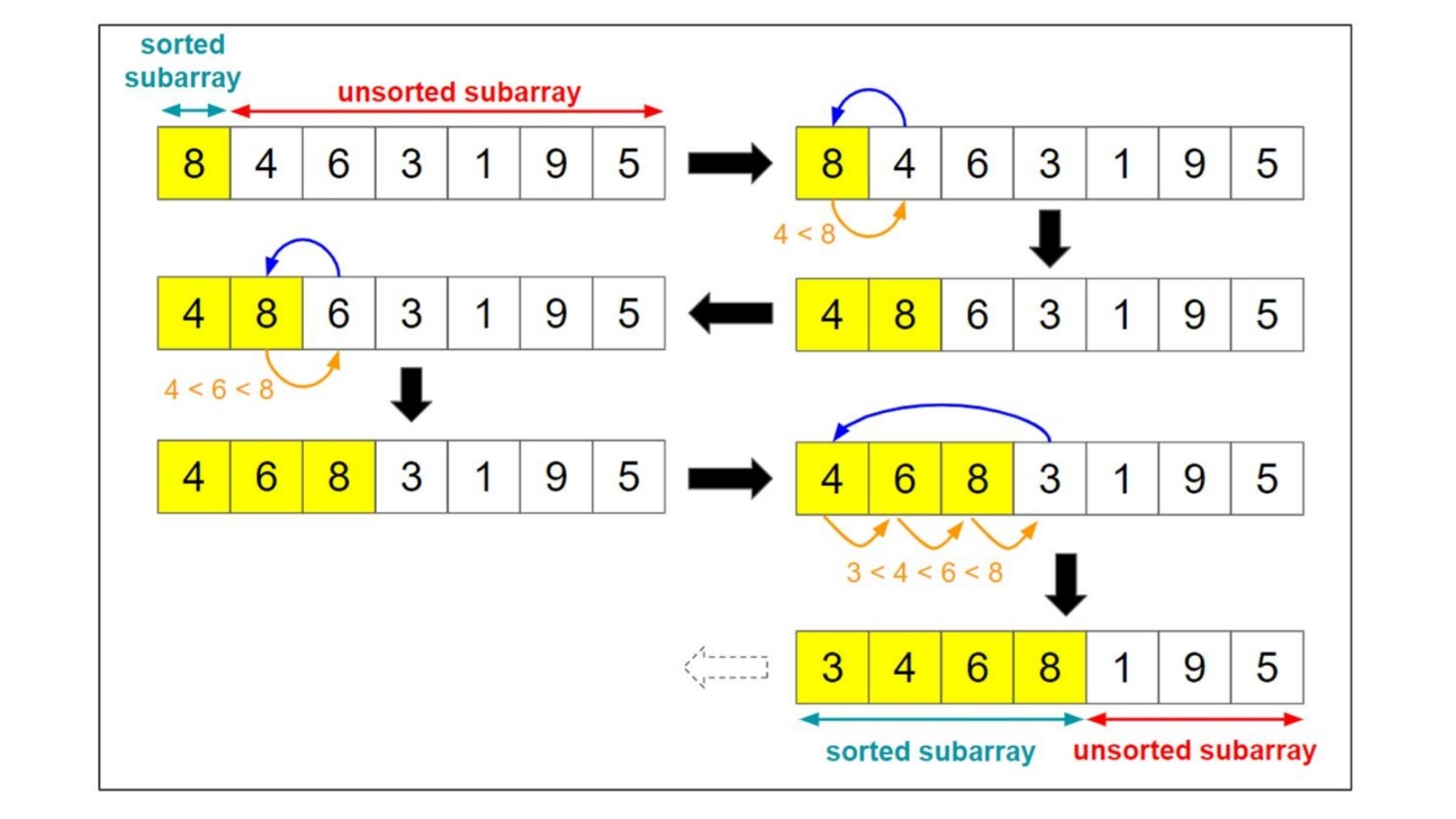
Bubble Sort

This is a very simple algorithm, it takes a number and compares it with its adjacent neighbor. Let’s say we are sorting the data structure in increasing order… we will start at the beginning and compare the first element to its neighbor. If the second element is larger in numeric value, a swap will be done.
Bubble sort is good for smaller datasets due to its quadratic time complexity of O(n^2), that is for its average case and worst case. Best case time complexity is if the array is already sorted, then it is O(n) time complexity.
This will be very slow for large datasets. Number of comparisons: N-1 comparisons (N = the size of the array)